Can This Music Relieve Your Stress and Help You Sleep?

Stress-management is practically a way of life these days.
What with inflammatory diets, increased exposure to environmental toxins, and the constant onslaught of negative news, it’s a wonder people can find any sense of relaxation at all!
Thankfully, there are many tools out there for reducing stress and its symptoms (like poor sleep).
One tool I’ve fallen in love with recently is a relatively new technology known as “binaural beats.” While binaural beats are often combined with similar sounds (flutes, nature sounds, etc.), they’re not the same as your average relaxing music track.
Binaural beats interact with your brain in fascinating ways that are not yet fully understood by science. What does seem clear, however, is that these tracks can have powerfully relaxing and calming effects on your brain and body.
Let’s take a closer look.
What Are Binaural Beats?
At its core, a binaural beat track consists of two tones of slightly different frequency.
Using headphones, one tone is played exclusively to the left ear, and the other to the right ear. When each ear hears a different frequency tone like this, your brain integrates the two frequencies and creates a third sound— the binaural beat.
When you listen to a binaural beat track, you end up “hearing” a tone that isn’t actually being played by the track itself! Rather, the tone is created in your brain as an oscillation of neural activity in a section of your brainstem known as the superior olivary nucleus.
This binaural beat is “heard” as a tone at the same frequency as the difference between the two frequencies played in each ear. For example, if one ear hears a tone of 110 Hz (cycles per second), while the other hears a tone of 100 Hz, the binaural beat created by the brain would be a frequency of 10 Hz (110 – 100 = 10).
“Binaural beat” tracks typically include other sounds as well, such as relaxing music, nature sounds, and “pink sound” (white noise equalized to be more pleasant to the ear).

How Can Binaural Beats Help You?
While most of the buzz around binaural beats is anecdotal, more and more studies are being published showing the health benefits of regularly listening to these tracks.
Research shows that, when combined with nature sounds, music, and pink sound, binaural beats may:
- Regulate neuron activity
- Improve sensory integration
- Enhance brain function
- Deepen relaxation
- Improve ease and quality of sleep
- Improve memory
- Increase learning capacity
- Induce meditative states
- Increase creativity
- Reduce stress
- Reduce depression (when combined with cognitive therapy)
- Improve pain management
Listening to binaural beats can also lead to increased synchronization between brain hemispheres and induce mental states similar to those of deep meditation and hypnagogic states (like right before falling asleep).
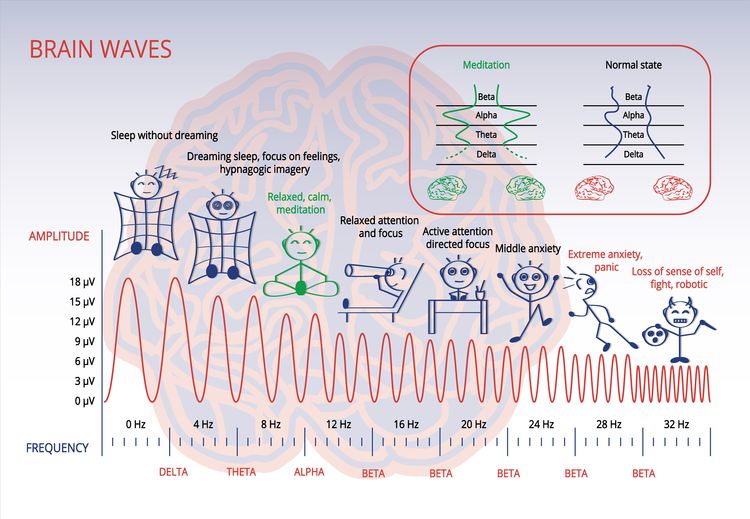
How Do Binaural Beats Work?
While scientists are not yet 100% sure how binaural beats influence mood and induce relaxation, some things are clear.
First and foremost, binaural beats influence your brain waves.
Your brain is a buzzing hive of electrical activity. This electrical activity organizes itself into measurable brain wave patterns that operate in different frequency ranges. The main ranges include: Delta (0.5-2 Hz), Theta (3-7 Hz), Alpha (8-13 Hz), Beta (14-25 Hz), and Gamma (26-40 Hz).
Decades of research points to these brain wave frequency ranges corresponding with different mind states. For example:
- Delta brainwaves occur during deep, dreamless sleep and are commonly associated with deep meditation and intuitive and spiritual connection.
- Theta brainwaves occur during REM sleep, the hypnagogic state, and during hypnosis, visualization, trance states, and deep meditation; they’re associated with deep meditation, insight, and visualization.
- Alpha brainwaves are associated with states of relaxed awareness, such as during light meditation, daydreaming, or when watching a movie. They also occur often in flow states of peak physical performance.
- Beta brainwaves are associated with states that require intellect, focus, concentration, alertness, analysis, and logic, such as work or social situations.
- Gamma brainwaves help us process the information received through our senses. They’re associated with heightened awareness, compassion, and creativity. Fun fact— they’re often found in abundance in the brains of Tibetan meditators!

Studies show that alpha-frequency binaural beats increase alpha brain waves, and beta-frequency beats increase concentration, alertness, memory, and focused attention. Delta and theta wave tracks can improve relaxation, increase creativity, induce meditative states, and help you fall asleep.
Binaural beats seem to be able to produce desirable mental states (e.g., relaxation, alertness, creativity, etc.) by guiding your brain to produce more of the brainwaves associated with these mental states. Binaural beats do this by taking advantage of a function of the brain known as the “electroencephalographic (EEG) frequency-following response.”
Basically, your brain adapts its brain-wave frequency to the frequency of the track you’re listening to.
While the “frequency-following response” phenomenon is well-documented, the measured changes in brain-wave frequency are usually quite small— some would say too small to cause the changes in consciousness associated with binaural beats.
In response to these points, other theories propose that binaural beats affect a region of the brain known as the extended reticular-thalamic activation system (ERTAS), which is involved with several brain functions associated with consciousness.
The idea is that binaural beats cause changes in brain-wave frequency, and the ERTAS receives this as a sign to induce different mental states.
As you can see, this stuff can get quite complex!
The essential point here is that we don’t yet know exactly how binaural beats affect the brain the way they do. While researchers and experts have some solid theories, there remains much room for research in this field.

Where Can I Try Binaural Beats?
Google “binaural beats” and you’ll find plenty of tracks, websites, and programs to choose from. YouTube is an especially rich resource.
A few sites I personally enjoy are MyNoise and iAwakeTechnologies. MyNoise is completely free and lets you customize your track to your heart’s content. iAwake has a lot of binaural beat-including tracks for sale and three free sample audios to try for yourself.
Remember: changing mental states is a subtle process; while binaural beats can certainly help shift your mental state, it’s not a simple switch!
The folks at The Monroe Institute recommend you relax and focus your attention on the track you’re listening to. The more you do so, the more likely you’ll experience its benefits.
NOTE: While binaural beats will be completely harmless for most people, some might want to avoid listening to these tracks, as they could cause negative side effects.
If you have a condition like epilepsy, an irregular heartbeat, cochlear hyperacusis, or synesthesia, consult a doctor or medical expert before trying out binaural beats.
Summary
The very concept of binaural beats may be a bit “out there” for some of you. Even still, I encourage you to try out these tracks for yourself! They can be powerful tools to help you relax, release stress, and improve your sleep.
